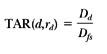TAR or Tissue Air Ratio
Tissue-Air Ratio
Tissue-air ratio
(TAR) was first introduced by Johns in 1953 and was
originally called the “tumor-air ratio.” At that time, this quantity was
intended specifically for rotation therapy calculations. In rotation therapy,
the radiation source moves in a circle around the axis of rotation, which is
usually placed in the tumor. Although the SSD may vary depending on the shape of
the surface contour, the source-axis distance remains constant.
Since the percent
depth dose depends on the SSD , the SSD correction to
the percent depth dose will have to be applied to correct for the varying SSD—a procedure that becomes cumbersome to apply
routinely in clinical practice. A simpler quantity—namely TAR—has been defined to remove the SSD dependence. Since the time of its
introduction, the concept of TAR has been refined to facilitate calculations not only for rotation therapy, but also for stationary isocentric
techniques as well as irregular fields.
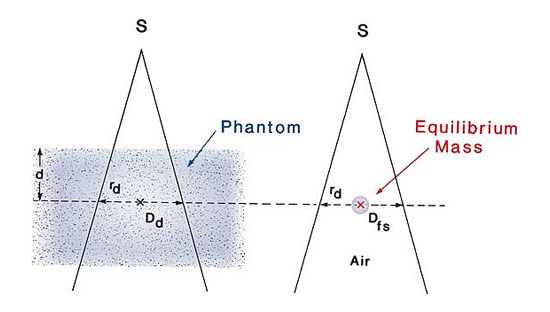
Tissue-air ratio may
be defined as the ratio of the dose (Dd) at a given point in the phantom to the dose in free
space (Dfs) at the same point.
This is illustrated in Figure 2 For a given quality
beam, TAR depends on depth d and field size
rd at that depth:
Fig 2: Illustration of the definition of tissue-air ratio (TAR). TAR(d,rd) = Dd/Dfs
Physics of Radiation Therapy, The, 5th Edition
Faiz M. Khan PhD
Professor Emeritus
- ۰ نظر
- ۱۹ شهریور ۹۴ ، ۰۹:۲۴