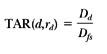Scatter Air Ratio
SARs are used for the purpose of calculating scattered dose in the medium. The computation of the primary and the scattered dose separately is particularly useful in the dosimetry of irregular fields.
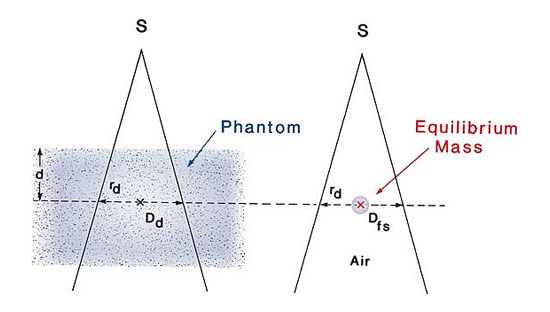
SAR may be defied as the ratio of the scattered dose at a given point in the phantom to the dose in free space at the same point. The SAR, like the TAR, is independent of the SSD but depends on the beam energy, depth, and field size.
Because the scattered dose at a point in the phantom is equal to the total dose minus the primary dose at that point, SAR is mathematically given by the difference between the TAR for the given field and the TAR for the 0 × 0 field
SAR (d, rd) = TAR (d, rd) - TAR (d,0)
Here TAR (d,0) represents the primary component of the beam.
Khan's The Physics of Radiation Therapy Fifth Edition
- ۰ نظر
- ۲۳ ارديبهشت ۹۵ ، ۱۰:۴۶